Problem description
Every day you are driving from your home to your work location. There are a number of alternative routes that you might use. You may think of these routes as a set of lines that connect nodes (=intersection points of routes). For every line (edge) we know the required travel time for getting from one end point to the other. What we don't know is the occurrence of roadworks or similar incidents that slow down traffic and hence cause delays.
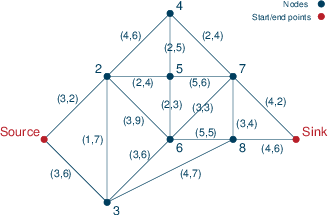
Figure 1: Road network
Figure Road network shows an example of a road network where the journey start and end points are marked as 'Source' and 'Sink' respectively. The label tuples (L,D) on the edges indicate the length (travel time) of an edge and the maximum delay D that may result from roadwork on this edge. In this data instance, the times in both directions for traveling along an edge are the same and the maximum delay in both senses is also the same, but in the general case the values might actually be different.
© 2001-2020 Fair Isaac Corporation. All rights reserved. This documentation is the property of Fair Isaac Corporation (“FICO”). Receipt or possession of this documentation does not convey rights to disclose, reproduce, make derivative works, use, or allow others to use it except solely for internal evaluation purposes to determine whether to purchase a license to the software described in this documentation, or as otherwise set forth in a written software license agreement between you and FICO (or a FICO affiliate). Use of this documentation and the software described in it must conform strictly to the foregoing permitted uses, and no other use is permitted.

