How to read this book
For a complete overview and introduction to modeling and solving with the FICO Xpress Optimization product suite, we recommend reading the entire document. However, readers who are only interested in certain topics, may well skip certain parts or chapters as shown in the following diagram.
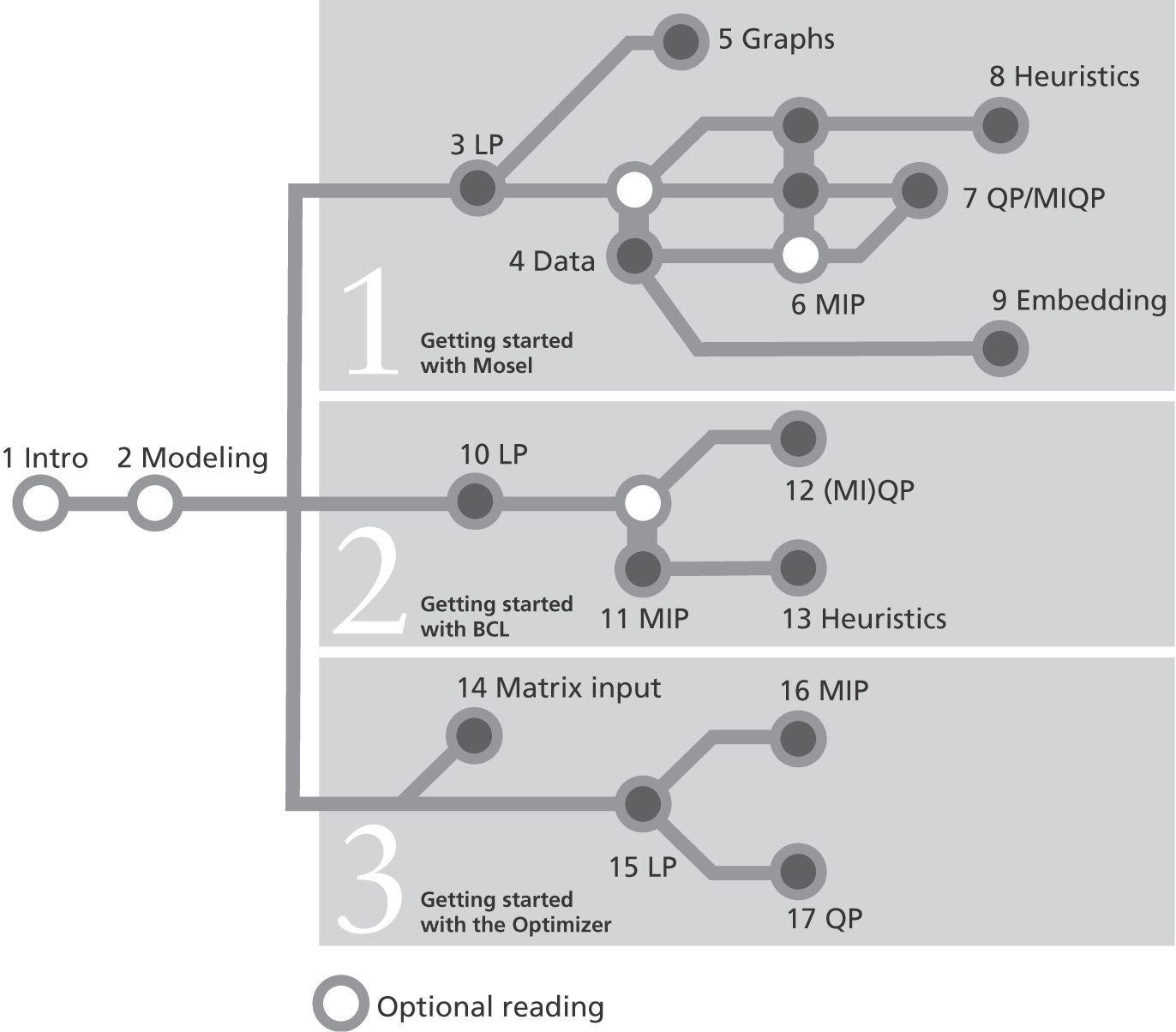
Figure 1.1: Suggested flow through the book
Using the Mosel language with Xpress Workbench
The approach presented in the first part of this book is recommended for first time users, novices to Mathematical Programming, and users who wish to develop and deploy new models quickly, supported by graphical displays for problem and solution analysis.
For example, if you wish to develop a Linear Programming (LP) model and embed it into some existing application, you should read the first four chapters, followed by Chapter 9 on embedding Mosel models.
To find out how to model and solve Quadratic Programming (QP) problems with Xpress, you should read at least Chapters 1-3, the beginning of Chapter 4 and then Chapter 7; for Mixed Integer Quadratic Programming (MIQP) also include Chapter 6 on Mixed Integer Programming (MIP).
To see how you may implement your own solution algorithms and heuristics in the Mosel language, we suggest reading Chapters 1-3, the beginning of Chapter 4, followed by Chapter 6 on MIP and then Chapter 8 on Heuristics.
Working in a programming language environment
Users who wish to develop their entire application in a programming language environment have two options, using the model builder library BCL or inputting their problem directly into Xpress Optimizer.
Users who are looking for modeling support whilst model execution speed is a decisive factor in their choice of the tool should look at the model builder library BCL. Due to the modeling objects defined by BCL, the resulting code remains relatively close to the algebraic model and is easy to maintain. BCL supports modeling of LP, MIP, and QP problems (Chapters 10-12). Model input with BCL may be combined with direct calls to Xpress Optimizer to define solution algorithms as shown with the example in Chapter 13.
The direct access to the Optimizer (discussed in the last part) is provided mainly for low-level integration with applications that possess their own matrix generation routines (Chapters 15-17 for LP, MIP, and QP problems), or to solve matrices given in standard format (MPS or LP) that were generated externally (Chapter 14). The possibility to directly access very specific features of the Optimizer is also appreciated by advanced users, mostly in the domain of research, who implement their own algorithms involving the solution of LP, MIP, or QP problems.

