task_serialize
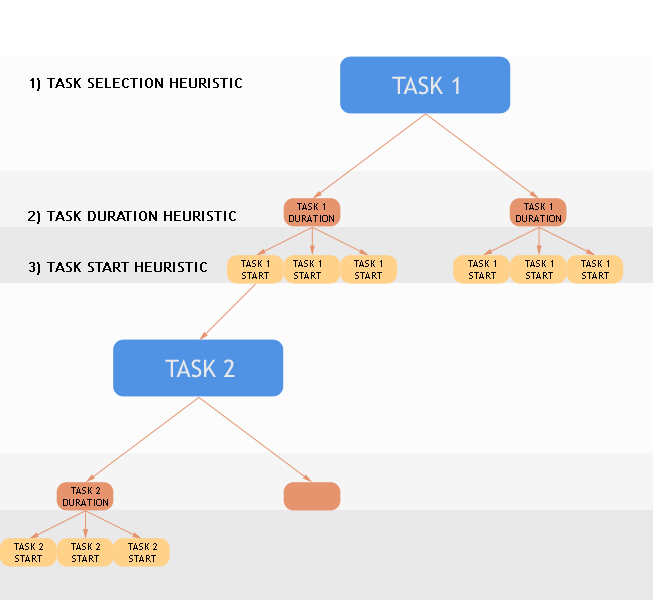
function task_serialize(taskSelector:string or function, durationHeuristic:string or function, startHeuristic:string or function, tasks:set of cptask) : cpbranching
function task_serialize(taskSelector:string or function, durationHeuristic:string or function, startHeuristic:string or function, tasks:array of cptask) : cpbranching
function task_serialize(taskSelector:string or function, durationHeuristic:string or function, startHeuristic:string or function, tasks:set of cptask, limit:integer) : cpbranching
function task_serialize(taskSelector:string or function, durationHeuristic:string or function, startHeuristic:string or function, tasks:array of cptask, limit:integer) : cpbranching
function task_serialize(taskSelector:string or function, durationHeuristic:string or function, startHeuristic:string or function, tasks:set of cptask, limit:integer, varOrder:integer) : cpbranching
function task_serialize(taskSelector:string or function, durationHeuristic:string or function, startHeuristic:string or function, tasks:array of cptask, limit:integer, varOrder:integer) : cpbranching
function task_serialize(taskSelector:string or function, durationHeuristic:string or function, startHeuristic:string or function, assignSelector:string or function, assignHeuristic:string or function, tasks:array of cptask, limit:integer, varOrder:integer) : cpbranching
function task_serialize(taskSelector:string or function, durationHeuristic:string or function, startHeuristic:string or function, assignSelector:string or function, assignHeuristic:string or function, tasks:set of cptask, limit:integer, varOrder:integer) : cpbranching
|
taskSelector
|
the task selector (pre-defined constant, name of user-defined function or reference to user-defined function)
|
||||||||||||
|
durationHeuristic
|
the task duration assignment heuristic (pre-defined constant, name of user-defined function or reference to user-defined function)
|
||||||||||||
|
startHeuristic
|
the task start time assignment heuristic (pre-defined constant, name of user-defined function or reference to user-defined function)
|
||||||||||||
|
assignSelector
|
a variable selection heuristic to choose among assignments of resources provided, produced, required or consumed by the task (pre-defined constant, name of user-defined function or reference to user-defined function)
|
||||||||||||
|
assignHeuristic
|
a value selection heuristic (pre-defined constant, name of user-defined function or reference to user-defined function)
|
||||||||||||
|
tasks
|
the set of tasks to be serialized.
|
||||||||||||
|
limit
|
discrepancy limit: value 0 means strictly following the branching scheme, positive values indicate the permissible number of deviations from the branching scheme. It can be set to
MAX_INT for no limitations.
|
||||||||||||
|
varOrder
|
the branching order of the variables resource assignment (A), start (S) and duration (D) of one task, values can be:
|
model "Tasks serialization example"
uses "kalis"
declarations
Masonry, Carpentry, Roofing, Windows, Facade, Garden, Plumbing,
Ceiling, Painting, MovingIn : cptask ! Declaration of tasks
Taskset : set of cptask
money_available : cpresource ! Resource declaration
end-declarations
forward function selectNextTask(tasks: cptasklist) : integer
! 'money_available' is a cumulative resource with max. amount of 29$
set_resource_attributes(money_available,KALIS_DISCRETE_RESOURCE,29)
! Limit resource availability to 20$ in the time interval [0,14]
setcapacity(money_available, 0, 14, 20)
! Setting the task durations and predecessor sets
set_task_attributes(Masonry , 7)
set_task_attributes(Carpentry, 3, {Masonry})
set_task_attributes(Roofing , 1, {Carpentry})
set_task_attributes(Windows , 1, {Roofing})
set_task_attributes(Facade , 2, {Roofing})
set_task_attributes(Garden , 1, {Roofing})
set_task_attributes(Plumbing , 8, {Masonry})
set_task_attributes(Ceiling , 3, {Masonry})
set_task_attributes(Painting , 2, {Ceiling})
set_task_attributes(MovingIn , 1, {Windows,Facade,Garden,Painting})
! Setting the resource consumptions
consumes(Masonry , 7, money_available)
consumes(Carpentry, 3, money_available)
consumes(Roofing , 1, money_available)
consumes(Windows , 1, money_available)
consumes(Facade , 2, money_available)
consumes(Garden , 1, money_available)
consumes(Plumbing , 8, money_available)
consumes(Ceiling , 3, money_available)
consumes(Painting , 2, money_available)
consumes(MovingIn , 1, money_available)
! Set of tasks to schedule
Taskset := {Masonry, Carpentry, Roofing, Windows, Facade, Garden,
Plumbing, Ceiling, Painting, MovingIn}
! Set the custom branching strategy using task_serialize:
! - the task serialization process will use the function
! "selectNextTask" to look for the next task to fix
! - it will use the "KALIS_MAX_TO_MIN" value selection heuristic
! to set the tasks duration variable
! - and the "KALIS_MIN_TO_MAX" value selection heuristic to set
! the start of the task
cp_set_branching(task_serialize(->selectNextTask,
KALIS_MAX_TO_MIN, KALIS_MIN_TO_MAX, Taskset))
! Find the optimal schedule (minimizing the makespan)
if 0 <> cp_schedule(getmakespan) then
cp_show_sol
else
writeln("No solution found")
end-if
!-------------------------------------------------------------
! **** Function to select the next task to schedule
function selectNextTask(tasks: cptasklist) : integer
write("selectNextTask : ")
declarations
Vset,Iset: set of integer
end-declarations
! Get the number of elements of "tasks"
listsize:= getsize(tasks)
! Set of uninstantiated variables
forall(i in 1..listsize)
if not is_fixed(getstart(gettask(tasks,i))) or
not is_fixed(getduration(gettask(tasks,i))) then
Vset+= {i};
end-if
if Vset={} then
returned:= 0
else
! Get the variables with max. degree
dmax:= max(i in Vset) getsize(getduration(gettask(tasks,i)))
forall(i in Vset)
if getsize(getduration(gettask(tasks,i))) = dmax then
Iset+= {i}; end-if
dsize:= MAX_INT
! Choose var. with smallest domain among those indexed by 'Iset'
forall(i in Iset)
if getsize(getstart(gettask(tasks,i))) < dsize then
returned:= i
dsize:= getsize(getstart(gettask(tasks,i)))
end-if
end-if
if returned <> 0 then
writeln(gettask(tasks,returned))
end-if
end-function
end-model
© 2001-2024 Fair Isaac Corporation. All rights reserved. This documentation is the property of Fair Isaac Corporation (“FICO”). Receipt or possession of this documentation does not convey rights to disclose, reproduce, make derivative works, use, or allow others to use it except solely for internal evaluation purposes to determine whether to purchase a license to the software described in this documentation, or as otherwise set forth in a written software license agreement between you and FICO (or a FICO affiliate). Use of this documentation and the software described in it must conform strictly to the foregoing permitted uses, and no other use is permitted.

