Structure of the Insight Python Application File Template
- Initially, you import your libraries and declare your data.
- Define the Load function that initializes all inputs.
- Define the Run function that initializes all results, and anything marked as requiring 'update after execution'.
These Python Load and Run functions call the FICO® Xpress Insight execution modes, for more see Execution Modes.
Template File
import pandas as pd
import xpress as xp
import xpressinsight as xi
import sys

|
Note: The
Insight Python module uses the pandas library and reflects that data naming convention. The documentation for the pandas library can be accessed at
https://pandas.pydata.org/.
|
@xi.AppConfig(name="Quick Start with Python", version=xi.AppVersion(1, 0, 0))
class InsightApp(xi.AppBase):
# Use type hints to declare the data model entities for the scenario.
# Inputs need to be initialized in the load mode(s).
# Entities are inputs if the manage attribute is xi.Manage.INPUT. This is the default, i.e., it can be omitted.
MyInteger: xi.types.Scalar(dtype=xi.integer, alias='My Integer', manage=xi.Manage.INPUT)
Indices: xi.types.Index(dtype=xi.integer, alias='Array Indices')
Input: xi.types.Series(index=['Indices'], dtype=xi.integer, alias='Input Array')
# Results need to be initialized in the run mode(s).
# Entities are results if the manage attribute is xi.Manage.RESULT.
Result: xi.types.Series(index=['Indices'], dtype=xi.real, manage=xi.Manage.RESULT, alias='Result Array')- The name declared in this line of code:
@xi.AppConfig(name="Quick Start with Python", version=xi.AppVersion(1, 0, 0))is utilized as the application name on the tile displayed in the Xpress Insight HOME page. - Also, in the example below, the scalar value assigned to the variable
MyIntegeris visible in the Entity Explorer next to the alias label.MyInteger: xi.types.Scalar(dtype=xi.integer, alias='My Integer', manage=xi.Manage.INPUT)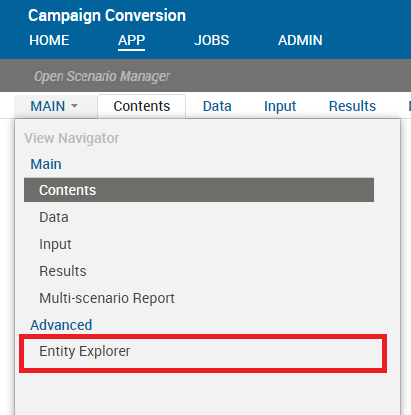
- Define the data value type (
dtype) for each entity. - Define an index for each Series and DataFrame—For example, the
inputseries references theindicieselement in the line above.Indices: xi.types.Index(dtype=xi.integer, alias='Array Indices') Input: xi.types.Series(index=['Indices'], dtype=xi.integer, alias='Input Array')
LOAD function and a
RUN function defined. These are shown in the template file immediately after the declarations.
@xi.ExecModeLoad(descr="Loads input data.")
def load(self):
# Scenario is being 'loaded' through Xpress Insight.
# Insight automatically populates the parameters with the values from the UI.
# Input entities will be captured and stored in the scenario.
self.Input = pd.read_csv('input.csv', index_col=['Indices'], squeeze=True)
self.Indices = self.Input.index
self.MyInteger = self.Indices.size
print("\nLoad mode finished.")
@xi.ExecModeRun(descr="Takes input data and uses it to compute the results.")
def run(self):
# Scenario is being 'run' through Xpress Insight.
# Insight automatically populates the parameters and inputs with the values from the UI.
# Result entities will be captured and stored in the scenario.
print('Scenario:', self.insight.scenario_name)
# Calculate the results data.
self.Result = self.Input * float(self.MyInteger)
print("\nRun mode finished.")
@xi.ExecMode(name="CUSTOM_RUN", descr="Custom run execution mode.", clear_input=False)
def my_custom_run_mode(self):
self.Result = self.Input * (self.MyInteger * 0.5)
print("Custom run mode finished.") Note that Indices: xi.types.Index(dtype=xi.integer, alias='Array Indices') will also be loaded as an input, as there is no manage attribute declared.
Load function
When the load function is executed (for example, when Load is selected on the Xpress Insight Scenario pill drop down menu), the entities declared as input data in the Python file (and any entities that are not declared) are loaded as input into the Xpress Insight database. For example, an entity declared in the load function as MyInteger: xi.types.Scalar(dtype=xi.integer, alias='My Integer', manage=xi.Manage.INPUT) will be loaded, because the last term in the declaration manage=xi.Manage.INPUT explicitly marks it as Insight input data.
Run function
Result: xi.types.Series(index=['Indices'], dtype=xi.real, manage=xi.Manage.RESULT, alias='Result Array')

|
Note: Advanced users can also create custom run modes.
|
Main function
if __name__ == "__main__":
# When the application is run in test mode (i.e., outside of Xpress Insight),
# first initialize the test environment, then execute the load and run modes.
app = xi.create_app(InsightApp)
sys.exit(app.call_exec_modes(["LOAD", "RUN"]))© 2001-2025 Fair Isaac Corporation. All rights reserved. This documentation is the property of Fair Isaac Corporation (“FICO”). Receipt or possession of this documentation does not convey rights to disclose, reproduce, make derivative works, use, or allow others to use it except solely for internal evaluation purposes to determine whether to purchase a license to the software described in this documentation, or as otherwise set forth in a written software license agreement between you and FICO (or a FICO affiliate). Use of this documentation and the software described in it must conform strictly to the foregoing permitted uses, and no other use is permitted.

