Upgrading from Mosel 3 to Mosel 4
Character encoding
Mosel is now working in UTF-8. This concerns
- the internal representation of text
- all external APIs (i.e. all Mosel libraries)
- the communication with the system via Unicode (Windows) or system encoding (Posix)
All streams and text files default to UTF-8. There is no impact on applications that only use pure ASCII (first 127 characters), but text data files and source code using other encodings might require conversions or tagging.
Please note that the remarks on character encoding in this document only refer to text file formats, no changes are required for other file types including spreadsheets or databases.
Character encoding — compatibility
If your model is no longer producing the expected output or not displaying correctly within IVE:
- Use the command 'xprnls info' to identify which encoding is used on your system
Example: output produced for western European Windows / 'latin' encoding (UK English):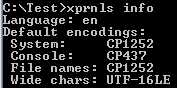
- Alternatively, use Xpress-IVE to display the system encoding from its menu entry Help » About Xpress-IVE.
- Specify the encoding (in model source and text data files in Mosel format) with the annotation !@encoding
- Convert text/string input and output via the enc: prefix to file names and streams or by using the conversion routines of the XPRNLS library or command tool (see paragraph 'Character encoding — conversion' below)
Character encoding — Example
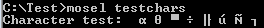
- Previous behaviour (Mosel 3 and older):
For the following Mosel model code
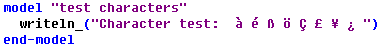
on a system with western European configuration the correct output is displayed within IVE but not at the console:
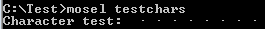
- New behaviour with Mosel 4 (the placeholder '.' is shown instead of characters that cannot be properly represented):
- Specifying the correct encoding at the beginning of the model source:
!@encoding CP1252 model "test characters" ...
results in this display: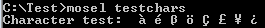
Character encoding — conversion
- Text format data files (other than the Mosel initializations format for which the !@encoding marker can be used) such as CSV files or files accessed via fopen that do not use UTF-8 encoding need to be converted with the 'enc:' prefix when accessing them from within a Mosel model.
Example:! Encoding names are operating system dependent, eg CP1252, ISO88591 fopen("enc:GB18030,testdata.txt", F_INPUT)
It is usually preferrable to specify the encoding used by a data file as shown above, but Mosel also implements shorthands for encodings configured on the system running the model.! Encoding aliases: ! raw, sys, wchar, fname, tty, ttyin, stdin, stdout, stderr initializations to "enc:sys,mmsheet.csv:testoutput.csv" ... end-initializations
Using the prefix enc:sys re-establishes the previous behaviour of Mosel, namely defaulting to the system encoding. - On the API level, you can use the XPRNLS library to convert to/from UTF-8 encoding:
- this library is platform independent and has no external dependency
- it handles encoding conversions between UTF-8 and local encodings
- it implements UTF-8/16/32(LE+BE), ISO-8859-1/15, ASCII, CP1252
- other supported encodings depend on the operating system
// Open a file using the C function 'fopen' with a file name // coming from Mosel f = fopen(XNLSconvstrto(XNLS_ENC_SYS,filename,-1,NULL),"r");
- Alternatively, you can use the XPRNLS command tool for converting the encoding of text files:
xprnls conv -f CP1252 -t UTF16 -o outfile.txt myfile.txt
© 2001-2026 Fair Isaac Corporation. All rights reserved. This documentation is the property of Fair Isaac Corporation (“FICO”). Receipt or possession of this documentation does not convey rights to disclose, reproduce, make derivative works, use, or allow others to use it except solely for internal evaluation purposes to determine whether to purchase a license to the software described in this documentation, or as otherwise set forth in a written software license agreement between you and FICO (or a FICO affiliate). Use of this documentation and the software described in it must conform strictly to the foregoing permitted uses, and no other use is permitted.

