provides
provides |
Purpose
Sets the minimal and maximal amount of resource provided by a task for a particular resource.
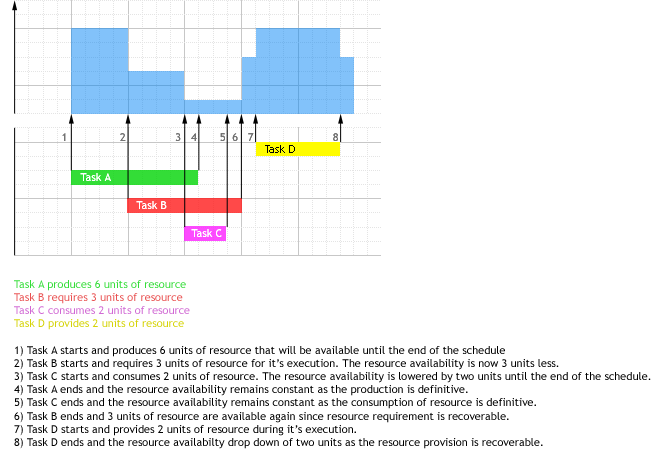
A task provides some amount of processing power for a resource during its execution. The capacity provided is considered as renewable which means that whenever the providing task ends, the provided capacity is no longer available. Note that a minimal amount of 0 is possible thus allowing modeling of alternative resources. The type of resource provision can be defined in several ways:
A task provides some amount of processing power for a resource during its execution. The capacity provided is considered as renewable which means that whenever the providing task ends, the provided capacity is no longer available. Note that a minimal amount of 0 is possible thus allowing modeling of alternative resources. The type of resource provision can be defined in several ways:
- By specifying a resource and a constant provision parameter 'provision'. In this case the resource provision is constant over the execution of the task.
- By specifying a resource and minimal 'minProv' and maximal 'maxProv' provision parameters: In this case the resource provision is a decision variable but is constant over the execution of the task.
- By specifying a cpresusage 'usage' (see resusage for further detail).
- By a set of alternative cpresusage 'optUsages': This makes it possible to model alternative resources. The type of resource provision is defined by the resource usage passed in argument (see resusage for further detail).
- By a set of alternative cpresusage 'optUsages', a minimal 'minalt' and a maximal 'maxalt' number of alternative resources that must be provided: Between [minalt..maxalt] alternative provisions from the set will be active which means that several resources will be chosen to be provided by the task. The type of resource provision is defined by the resource usage passed in argument (see resusage for further detail).
Synopsis
procedure provides(task:cptask, provision:integer, resource:cpresource)
procedure provides(task:cptask, minProv:integer, maxProv:integer, resource:cpresource)
procedure provides(task:cptask, usage:cpresusage)
procedure provides(task:cptask, optUsages:set of cpresusage)
procedure provides(task:cptask, optUsages:set of cpresusage, minalt:integer, maxalt:integer)
Arguments
|
task
|
the task
|
|
provision
|
constant positive resource consumption
|
|
minProv
|
minimal resource consumption
|
|
maxProv
|
maximal resource provision
|
|
resource
|
the resource to be provided
|
|
usage
|
the resource usage
|
|
optUsages
|
the set of alternatives resource provision
|
|
minalt
|
minimal number of resources that must be provided
|
|
maxalt
|
maximal number of resources that may be provided
|
Example
The following example illustrates this:
model "Producer Consumer"
uses "kalis"
declarations
Masonry, Carpentry, Roofing, Windows, Facade, Garden, Plumbing,
Ceiling, Painting, MovingIn : cptask ! Declaration of tasks
money_available : cpresource ! Resource declaration
end-declarations
! 'money_available' is a cumulative resource with max. amount of 29$
set_resource_attributes(money_available,KALIS_DISCRETE_RESOURCE,29)
! Limit resource availability to 20$ in the time interval [0,14]
setcapacity(money_available, 0, 14, 20)
! Setting the task durations and predecessor sets
set_task_attributes(Masonry , 7 )
set_task_attributes(Carpentry, 3, {Masonry} )
set_task_attributes(Roofing , 1, {Carpentry} )
set_task_attributes(Windows , 1, {Roofing} )
set_task_attributes(Facade , 2, {Roofing} )
set_task_attributes(Garden , 1, {Roofing} )
set_task_attributes(Plumbing , 8, {Masonry} )
set_task_attributes(Ceiling , 3, {Masonry} )
set_task_attributes(Painting , 2, {Ceiling} )
set_task_attributes(MovingIn , 1, {Windows,Facade,Garden,Painting})
! Setting the resource consumptions
consumes(Masonry , 7, money_available )
consumes(Carpentry, 3, money_available )
consumes(Roofing , 1, money_available )
consumes(Windows , 1, money_available )
consumes(Facade , 2, money_available )
consumes(Garden , 1, money_available )
consumes(Plumbing , 8, money_available )
consumes(Ceiling , 3, money_available )
consumes(Painting , 2, money_available )
consumes(MovingIn , 1, money_available )
! Find the optimal schedule (minimizing the makespan)
if cp_minimize(getmakespan) then
cp_show_sol
else
writeln("No solution found")
end-if
end-model
Related topics

