Composable Architectures: Why Now and What’s Next
Composable architectures are driving IT’s evolution by enabling greater flexibility, scalability and resilience

Composable architectures have emerged as the cornerstone of modern enterprise innovation. As organizations contend with market disruptions, legacy integration challenges, and relentless demands for agility, composable architectures provide both a philosophy and a technical foundation for building resilient, scalable, and adaptable platforms. This post explores what is driving the need for composable architectures, defines the concept and its core principles, examines where the industry stands today, and considers future trends, culminating with how FICO is harnessing composable architecture to power FICO Platform.
What Is Driving the Need for Composable Architectures?
IT departments across industries are in the midst of a profound transformation, fueled by several converging factors:
- Market Disruption: The pace and magnitude of market disruptions have accelerated dramatically. Technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are reshaping industries overnight. The COVID-19 pandemic forced organizations to rethink their operations and accelerate digital transformation. Enterprises are now expected to respond to change at lightning speed, with little tolerance for slow adaptation.
- Hyper-Personalization: Customer expectations have shifted from generic offerings to highly personalized experiences. Whether in financial services, retail or healthcare, businesses must now tailor products, recommendations, and interactions to the unique needs of individuals. This demand pushes IT teams to build flexible, granular systems capable of rapid configuration and deployment.
- Legacy and Modern System Integration: The average enterprise is a patchwork of legacy systems, modern cloud platforms and cutting-edge microservices. Integrating these disparate technologies remains a thorny challenge. Organizations want the innovation and scalability of cloud-native services while preserving the value and reliability of legacy investments.
- Speed and Operational Risk: Time-to-market pressures mean organizations must deliver new capabilities quickly, often with minimal disruption. Business leaders expect IT departments to support faster launches, continuous improvement, and rapid experimentation — without increasing operational risk.
These interconnected drivers create an environment where traditional, monolithic approaches to application development and IT infrastructure simply cannot keep pace. The answer, increasingly, lies in composable architectures.
Defining Composable Architecture
At its core, a composable architecture is a collection of modular, interoperable components or services. Rather than building applications as single, monolithic entities, composable architectures break them into finely grained building blocks that can be assembled, disassembled, and reassembled in countless ways—enabling composability within the business.
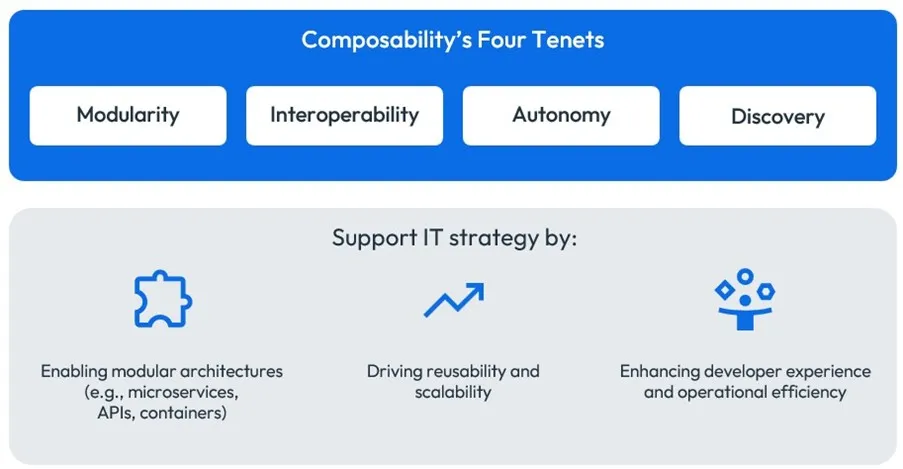
Four Pillars of Composability:
- Modularity: Every application or service is deconstructed into discrete modules, each encapsulating distinct functionality. Modularity enables abstraction, isolation and reuse, making it easier to update, replace or repurpose components as needs evolve.
- Interoperability: Components communicate effectively through well-defined interfaces, typically APIs. This ensures that modules can work together, regardless of their underlying technology or domain.
- Autonomy: Each module is designed to function independently, minimizing interdependencies. This independence is crucial for resilience — if one service fails, others remain unaffected, ensuring business continuity.
- Discovery: Modules must be discoverable so developers and systems can find, integrate and reuse them as needed. API-driven discovery frameworks facilitate this by making interfaces visible and accessible.
Composable architectures are not merely a technical strategy — they represent a paradigm shift in how organizations approach problem-solving. By decomposing business problems into refined units of work, enterprises can adapt quickly to change, reconfigure systems in response to new demands and innovate more rapidly.
Industry Status: From Mainframes to Microservices to Composability
The journey toward composable architecture mirrors the evolution of IT over the past three decades.
The era of mainframes and monoliths gave way to client-server architectures, which distributed workloads but often led to complex, tightly coupled systems.
The rise of cloud computing and microservices signaled a new wave of distributed, loosely coupled applications. These technologies enabled greater scalability and flexibility — but not without introducing new integration and observability challenges.
Today, composable architectures represent the next logical step. Modern platforms are built from modular services, exposed through APIs, and orchestrated via CI/CD pipelines and automation frameworks. Organizations strive for cloud-native solutions, yet remain wary of vendor lock-in and the need for interoperability across multiple providers (AWS, Azure, GCP, private clouds).
IT departments are at a crossroads. Many enterprises have begun the journey toward composability, but few have fully realized its potential. Most organizations operate hybrid environments, balancing legacy systems with modern cloud services. Challenges remain — especially in discovery, integration, and governance — but the momentum is unmistakable.
Building Your Future on a Composable Architecture
Several trends are set to shape the future of composable architectures:
- API-First Development: Successfully leveraging composable architecture within your business depends on clear, robust APIs that serve as contracts between modules. As organizations adopt API-first strategies, integration becomes simpler, test-driven development becomes standard, and cross-domain collaboration accelerates.
- Domain-Driven Design: Increasingly, IT teams are abstracting business knowledge into reusable assets — features, strategies, decision models — that can be shared and repurposed across the enterprise. Domain-driven abstraction allows organizations to compose solutions that directly reflect business objectives.
- Observability and Automation: As ecosystems grow in complexity, observability frameworks will need to track both system and business metrics. Automation of testing, deployment, and operations (via CI/CD) will become more sophisticated, enabling continuous integration and delivery across domains.
- Agentic Architectures: The next frontier lies in agentic systems that decompose workloads into self-contained units, capable of autonomous decision-making and problem-solving. These systems leverage business composability to orchestrate complex workflows, optimize outcomes, and respond dynamically to changing conditions.
FICO Platform: Built on a Composable Architecture
FICO, a leader in decision management and analytics, has embraced composable architecture as the foundation of our FICO Platform. Over the past three decades, FICO has refined the art of decision management by breaking processes into smaller units, abstracting business logic as reusable assets, and assembling these components to drive portfolio outcomes.
Core Principles in Practice
- Decision Management as a Composable Asset: FICO treats business logic — not just software — as an asset. By abstracting domain knowledge from runbooks and manuals into composable, reusable components, FICO empowers organizations to repurpose their knowledge across varied use cases.
- Granularity and Flexibility: FICO Platform enables users to configure composable flows, integrating services managed within FICO Platform and exposing them as modular solutions for specific business problems. These flows are domain-driven, allowing composition and communication between multiple workflows — such as retail lending sharing information with application fraud detection.
- Prepackaged Solutions and Modular Deployment: FICO’s asset-based approach allows rapid deployment of solutions, freeing users from the burden of underlying mechanisms. Existing logic and patterns can be reused, so organizations do not have to transform everything at once — they can evolve iteratively and strategically.
- CI/CD Integration: FICO Platform exposes continuous integration and deployment concepts not only to IT systems but also to business domains. Customers can continuously integrate and deploy updates in seconds, minimizing disruption and maximizing agility.
- Interoperable Ecosystems: FICO Platform supports hybrid environments, including cloud-native services, legacy systems, and customer-managed infrastructure. API-first, contract-based development ensures seamless interoperability and future-proof scalability.
Real-World Impact
Consider a major FICO customer that required seamless integration with their GitOps environment for automated deployments — a hybrid model where authoring occurred in the cloud but execution was local. FICO’s composable architecture enabled integration using Jenkins or Argo workflows, supporting both cloud and on-premise operations.
Another example is a leading video game company handling billions of daily events. By leveraging FICO Platform services authored in the cloud and integrating them with other cloud-hosted and local services within its composable business flow, the company optimized domain content reuse and operational flexibility at scale.
Key Takeaways: The Path Forward
Composable architecture is not a destination but a journey. It enables organizations to:
- Break business problems into manageable, reusable components
- Adapt quickly to disruption and changing market needs
- Integrate legacy and modern systems for maximum value
- Accelerate innovation, reduce operational risk, and ensure resilience
- Align IT strategies with business objectives through domain-driven design
By adopting approach based on a composable architecture, organizations will find themselves better equipped to navigate uncertainty, experiment boldly, and deliver personalized, impactful experiences at scale. FICO’s commitment to enabling business composability ensures its customers remain at the forefront of this evolution, leveraging the power of modularity, interoperability, autonomy, and discovery to drive lasting business value.
In the words of modern IT architects, “Design for modularity, validate through testing, and let domain-driven thinking guide every decision.” The future belongs to those who can compose, recompose, and adapt — one building block at a time.
How FICO Platform Gives You the Advantage of Composable Architecture
Popular Posts

Average U.S. FICO Score at 717 as More Consumers Face Financial Headwinds
Outlier or Start of a New Credit Score Trend?
Read more
Average U.S. FICO® Score at 716, Indicating Improvement in Consumer Credit Behaviors Despite Pandemic
The FICO Score is a broad-based, independent standard measure of credit risk
Read more
Business and IT Alignment is Critical to Your AI Success
These are the five pillars that can unite business and IT goals and convert artificial intelligence into measurable value — fast
Read moreTake the next step
Connect with FICO for answers to all your product and solution questions. Interested in becoming a business partner? Contact us to learn more. We look forward to hearing from you.
