Simulation and Optimization: Unlocking Better Decisions
Simulation and optimization are two different technology approaches that can dramatically improve the results of your decision strategies and improve customer centricity

As businesses strive to meet ever-increasing expectations for personalization, speed, and transparency, two powerful tools have emerged at the forefront of decision-making: simulation and optimization.
But what are simulation and optimization? How do they work, and what sets them apart? More importantly, how can you use them to deliver the best possible results for your customers and your business? Let’s dive deep into these concepts, explore their practical applications, and see how they’re already transforming leading organizations.
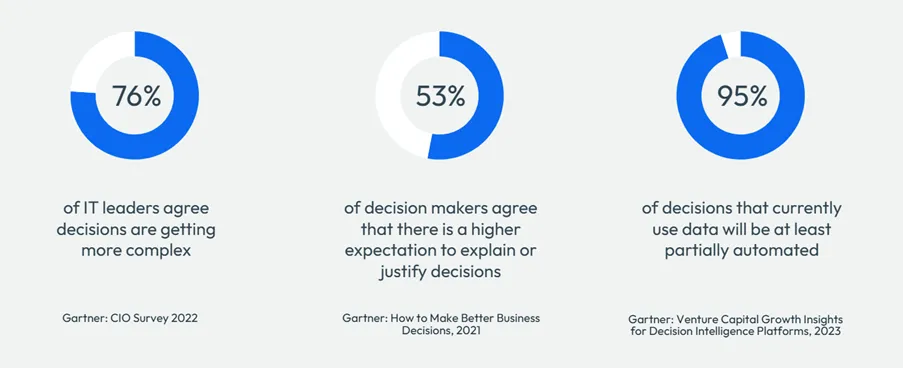
The Rising Complexity of Modern Decisions
Every day, businesses make thousands or millions of decisions for their customers. From approving loans and setting interest rates to detecting fraud or managing inventory, these choices are rarely straightforward. The complexity stems from several sources:
- Dynamic Economic Landscape. Rapid economic changes — from fluctuating inflation to shifting recession risks — create cascading effects on businesses and customers alike. In this volatile environment, strategic decisions must be resilient and adaptable to remain effective across varying economic conditions.
- Regulatory scrutiny. Decisions must be fair and justifiable. Regulators require transparency, internal audit teams demand proof, and customers expect clear explanations when things don’t go their way.
- Automation and personalization. With the rise of hyper-personalization, customers expect prompt, tailored offers—automatically delivered at scale.
Meeting these demands requires more than human intuition. It calls for robust, scalable systems that put the customer at the center, ensuring every decision is explainable and aligned with both business goals and regulatory requirements.
Simulation: Seeing the Future Before It Happens
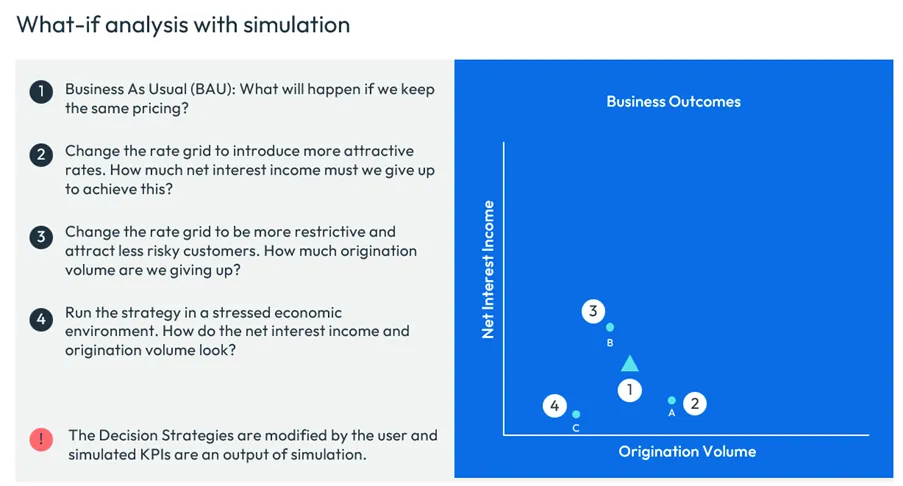
Imagine you could test your strategies before they ever touch a live customer. Simulation provides that sandbox, using a digital twin, a virtual duplicate environment to simulate, forecast, and assess impacts in advance.
A simulation models how different decisions would play out under various scenarios, using historical data and predictive analytics. By running decision models through this digital twin, you can:
- Simulate outcomes measured via key performance indicators (KPIs) like profit, risk exposure, and customer satisfaction.
- Identify unintended consequences before rolling out new strategies.
- Create alternate economic environments to simulate how current strategies perform under stress
- Collaborate across teams, ensuring everyone—from risk managers to operations leaders—understands the impact on their priorities.
Let’s look at some concrete examples to bring these ideas to life.
Loan Originations: Simulating Decisions for Maximum Impact
Consider a customer, Sam, applying for a loan. Sam has a FICO Score of 730 and a “thick file,” meaning a rich credit history. Let’s assume the business has three possible decision choices:
- Approve the loan at 6% APR
- Approve at a less favorable 6.5% APR
- Decline the application
From Sam’s perspective, the first offer is most attractive. For the business, profitability depends on how likely Sam is to accept each offer. Approving at 6% APR might yield a 90% take-up rate, resulting in $250,000 expected profit, while approving at 6.5% APR might yield an 80% take-up rate, resulting in $200,000 expected profit. In this simple example, approving at 6% APR is the best decision for both Sam and the business. While this is easy to do for one customer, when you're dealing with millions of customers, calculating this impact becomes virtually impossible through conventional means—that's where simulation becomes indispensable.
With simulation, the business can analyze performance of decision strategies on KPIs at scale across their customer portfolio. The business can define KPIs ranging from P&L metrics to risk metrics, to regulatory metrics and even operational metrics.
KPIs: Aligning Stakeholders Through Simulation
Different roles care about different KPIs. Portfolio managers may focus on economic profit and net interest income. Risk managers might worry about total exposure. Operations managers need to know how many manual reviews a strategy will trigger. Simulation empowers all stakeholders to see how decisions affect their work, preventing misalignment and nasty surprises.
When simulation is introduced early in the process, teams can iterate quickly, testing new strategies in a safe environment.
Scenario Planning: Facing the Unknown
Simulation shows you how decision strategies perform under different economic conditions. By simulating recessionary environments or rapid market changes, organizations can prepare for the worst and seize opportunities in the best-case scenarios.
Applications Across the Credit Lifecycle
The same principles apply elsewhere. In credit line management, simulation helps you balance growth and risk, revealing the best strategies before you commit. In fraud management, you can simulate how changing a score threshold would affect the rate of false positives—minimizing hassle for legitimate customers while catching more fraudsters.
Going back to the loan origination example above, simulation lets you understand the potential business outcomes across thousands of segments, delivering personalized offers that meet your company’s objectives. For instance, you might want to lower rates to attract more customers. Simulation shows whether this increases volume at the expense of net interest income, allowing you to find the right balance.
Optimization: Finding the Best Path Forward
While simulation lets you test “what ifs”, optimization goes a step further: it actually determines the best possible course of action based on your objectives and constraints. Setting an optimization problem involves clarifying your objectives, options, data and other decision variables.
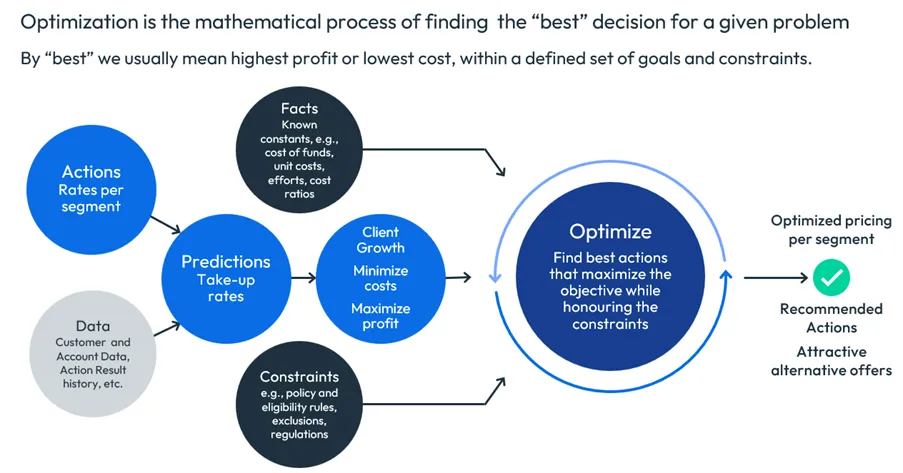
How Optimization Works
Optimization involves defining actions (like interest rates or approval thresholds), gathering data about customer segments and historical results, incorporating predictions (or predictive models) how customers will behave. The goal may be to:
- Maximize profit
- Minimize costs
- Achieve a target volume
- Reduce risk exposure
Regulatory and business constraints can be built into the model: you might need to avoid offering rates below a certain threshold, or ensure fair lending practices. Mathematically, the optimization engine crunches the numbers, producing recommended actions for each segment while calculating the KPIs of interest.
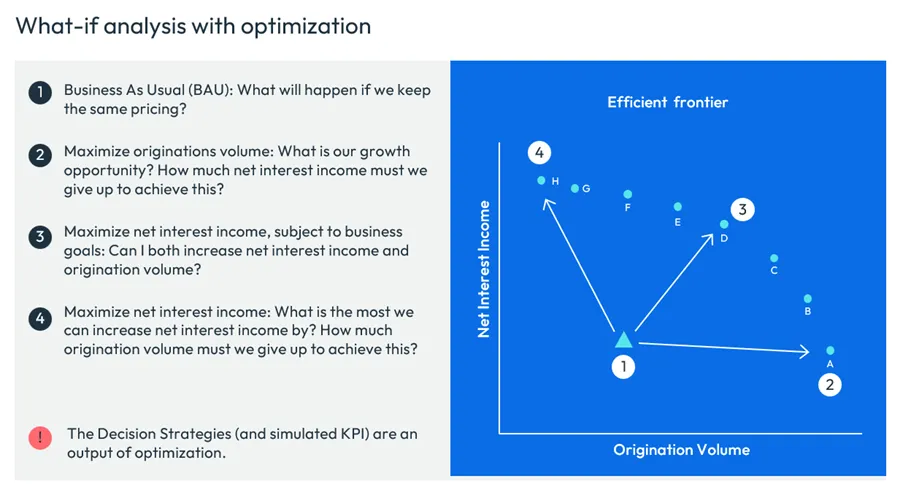
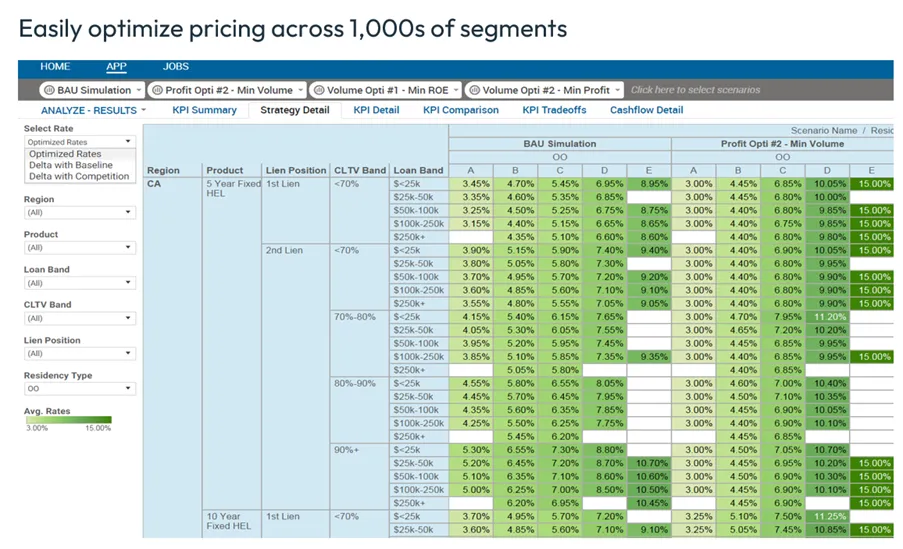
Pricing Optimization: A Real-World Example
Let’s revisit the loan pricing scenario. Suppose you have a table specifying interest rates for different FICO® Scores and loan types (auto loan, home equity line, mortgage, etc.). Higher scores get lower rates, and shorter loan durations also mean lower rates. As more factors (region, lien position, loan band) are added, the table grows complex.
Optimization is used to set the best pricing strategy for every segment, considering predicted take-up rates, business constraints, and your chosen objective function. The output: a refined, actionable pricing table ready for deployment.
Importantly, when offering real-time pricing, it’s best to give customers alternative offers—rather than a single take-it-or-leave-it choice—boosting engagement and satisfaction.
Simulation vs. Optimization: What’s the Difference?
Let’s clarify the distinction:
- Simulation lets you test strategies and calculates resulting KPIs, generating many data points for each decision scenario. It’s about exploring outcomes and understanding sensitivity to changes.
- Optimization calculates the strategies and KPIs simultaneously, producing an efficient frontier of optimal solutions under current assumptions. It’s about finding the best possible trade-offs, given your goals and constraints.
The magic happens when you combine both: after finding an optimal point, you use simulation to perform sensitivity analysis, revealing how robust your solution is to changes in input data. If a solution proves highly sensitive, perhaps it should be reconsidered. This helps you make the best trade-offs and understand the inherent compromises.
“There are no solutions, only tradeoffs”
Thomas Sowell, A Conflict of Visions: Ideological Origins of Political Struggles
Real-World Success Stories
Theory is compelling—but real-world examples show why simulation and optimization matter.
- Vitality, a leading health and life insurance provider based in the UK, is leveraging the FICO® Business Outcome Simulator (BOS to predict the outcomes of rule changes in real time, allowing the company to make data-driven decisions. The transition from legacy systems to FICO Platform has opened up new opportunities for Vitality to continue innovating.
- Česká spořitelna leverages optimization for loan pricing, limit management, and collections. After the pandemic, they developed early collection strategies that reduced operational efforts by 25% and freed staff to help customers under stress. Their approach earned them a FICO Decision Award in 2021, and their journey highlights the importance of courage, data quality, and stakeholder engagement in driving change.
- A major global financial institution adopted FICO’s loan pricing optimizer and saw a 26% increase in portfolio profit, a 29% increase in new sales, and a staggering $57 million boost in first-year revenue.
When to Use Simulation, Optimization, or Both?
- Use simulation whenever you change decision strategies, especially in complex processes at scale. Validate impacts, catch unintended consequences, and foster collaboration among stakeholders.
- Use optimization when you have competing goals and need better solutions. Ensure your strategy meets quality criteria within business constraints and adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
- Combine the two for maximum effect: optimization identifies the most promising options to pursue, while simulation reveals the impacts and sensitivities of your chosen strategies.
The ability to simulate and optimize is transforming how organizations operate. It brings together data, analytics, and human expertise, creating systems that are not only more efficient but also fairer, more transparent, and more responsive to customer needs.
Conclusion: Putting Customers at the Center of Every Decision
Simulation and optimization are not just technical buzzwords — they’re the cornerstone of modern, customer-centric business strategy. With the help of FICO Platform, organizations can automate, personalize, and justify millions of decisions, all while improving outcomes for their customers and meeting regulatory expectations.
By building robust simulations and optimization models, companies can iterate strategies quickly, adapt to changing economic conditions, and always keep the customer at the heart of every choice. In a world of uncertainty and rapid change, these tools provide the confidence and clarity needed to make better decisions—every time.
How FICO Can Bring the Power of Simulation and Optimization to Your Business
Popular Posts

Average U.S. FICO Score at 717 as More Consumers Face Financial Headwinds
Outlier or Start of a New Credit Score Trend?
Read more
Average U.S. FICO® Score at 716, Indicating Improvement in Consumer Credit Behaviors Despite Pandemic
The FICO Score is a broad-based, independent standard measure of credit risk
Read more
Average U.S. FICO® Score stays at 717 even as consumers are faced with economic uncertainty
Inflation fatigue puts more borrowers under financial pressure
Read moreTake the next step
Connect with FICO for answers to all your product and solution questions. Interested in becoming a business partner? Contact us to learn more. We look forward to hearing from you.
